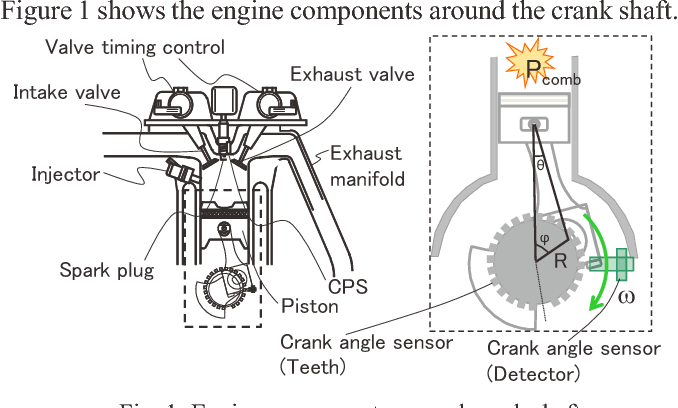
Crank angle is the angle of rotation of the crankshaft in an engine. The crankshaft is the part of the engine that converts the up and down motion of the pistons into circular motion. The crank angle is important because it determines the position and movement of the pistons, valves, and spark plugs in the engine. The crank angle also affects the engine timing, performance, and efficiency.
The crank angle sensor is a device that measures the crank angle and sends a signal to the engine control unit (ECU). The ECU is the computer that controls the engine functions, such as fuel injection, ignition, and emission. The crank angle sensor helps the ECU to adjust the engine timing and optimize the engine performance.
In this article, we will explain everything you need to know about the crank angle sensor, including its relationship to the engine cycle, its applications, and its related problems.
Relationship between crank angle and the engine cycle
The engine cycle is the process of converting fuel and air into power and exhaust in an engine. There are two types of engine cycles: four-stroke and two-stroke. Each type of engine cycle has a different number of crank angles and piston strokes.
Four-stroke engine cycle
A four-stroke engine cycle consists of four piston strokes and two crankshaft revolutions. The four piston strokes are intake, compression, power, and exhaust. The intake stroke occurs when the piston moves down and the intake valve opens, allowing air and fuel to enter the cylinder.
The compression stroke occurs when the piston moves up and the intake valve closes, compressing the air and fuel mixture. The power stroke occurs when the piston moves down and the spark plug ignites the compressed mixture, creating a force that pushes the piston down. The exhaust stroke occurs when the piston moves up and the exhaust valve opens, releasing the burned gases from the cylinder. The crank angle sensor measures the crank angle at each piston stroke and sends a signal to the ECU, which then controls the opening and closing of the valves and the firing of the spark plugs.
Two-stroke engine cycle
A two-stroke engine cycle consists of two piston strokes and one crankshaft revolution. The two piston strokes are compression and power. The compression stroke occurs when the piston moves up and the intake port opens, allowing air and fuel to enter the crankcase.
The power stroke occurs when the piston moves down and the spark plug ignites the compressed mixture, creating a force that pushes the piston down. The exhaust port opens and the burned gases are expelled from the cylinder. The crank angle sensor measures the crank angle at each piston stroke and sends a signal to the ECU, which then controls the firing of the spark plug.
The crank angle sensor can measure the crank angle in different ways, such as using a magnetic, optical, or hall effect sensor. The crank angle sensor is usually located near the crankshaft pulley or the flywheel. The crank angle sensor can have different numbers of teeth or slots, depending on the type and design of the engine.
Applications of crank angle sensor
The crank angle sensor has many applications in the engine, such as:
- Engine timing: The crank angle sensor helps the ECU to adjust the engine timing, which is the synchronization of the piston, valve, and spark plug movements. The engine timing affects the engine power, efficiency, and emission. The crank angle sensor tells the ECU when to open and close the valves and when to fire the spark plugs, based on the crank angle and the engine speed. The ECU can also adjust the valve timing and the ignition timing, depending on the engine load and condition.
The valve timing is the timing of the opening and closing of the intake and exhaust valves. The ignition timing is the timing of the firing of the spark plugs. The crank angle sensor helps the ECU to optimize the engine timing and improve the engine performance and fuel economy.
- Engine performance analysis: The crank angle sensor helps the ECU to analyze the engine performance, such as the engine speed, torque, power, and efficiency. The ECU can use the crank angle sensor data to calculate the engine speed, which is the number of revolutions per minute (RPM) of the crankshaft. The ECU can also use the crank angle sensor data to calculate the engine torque, which is the force that the engine produces to rotate the crankshaft.
The ECU can also use the crank angle sensor data to calculate the engine power, which is the rate at which the engine produces work. The ECU can also use the crank angle sensor data to calculate the engine efficiency, which is the ratio of the output power to the input fuel and air. The crank angle sensor helps the ECU to monitor and improve the engine performance and reduce the engine wear and tear.
- Engine diagnostics: The crank angle sensor helps the ECU to diagnose the engine problems, such as misfiring, poor fuel economy, and difficulty starting the engine. The ECU can use the crank angle sensor data to detect any abnormal or irregular crank angle signals, which may indicate a faulty crank angle sensor or a problem with the engine components. The ECU can also use the crank angle sensor data to compare the actual engine timing with the desired engine timing, which may indicate a problem with the valve timing or the ignition timing. The ECU can also use the crank angle sensor data to measure the engine compression, which may indicate a problem with the piston rings, the cylinder head, or the head gasket. The crank angle sensor helps the ECU to identify and troubleshoot the engine problems and to alert the driver with a warning light or a code.
Problems related to crank angle sensor
The crank angle sensor is an essential part of the engine, but it can also cause some problems if it is faulty or damaged. Some of the common problems related to the crank angle sensor are:
- Faulty crank angle sensor: The crank angle sensor can become faulty or damaged due to various reasons, such as wear and tear, corrosion, dirt, moisture, heat, vibration, or electrical interference. A faulty crank angle sensor can produce inaccurate or erratic crank angle signals, which can confuse the ECU and affect the engine timing and performance.
A faulty crank angle sensor can also cause the ECU to store an error code, which can be read by a scan tool or a code reader.
- Misfiring engine: A misfiring engine is an engine that does not fire properly or at the right time. A misfiring engine can cause poor engine performance, reduced power, increased fuel consumption, and increased emission. A misfiring engine can be caused by a faulty crank angle sensor, which can disrupt the engine timing and cause the spark plugs to fire at the wrong time or not at all. A misfiring engine can also damage the catalytic converter, which is a device that reduces the harmful gases from the exhaust.
- Poor fuel economy: Poor fuel economy is the condition when the engine consumes more fuel than normal. Poor fuel economy can cause increased fuel costs and environmental impact. Poor fuel economy can be caused by a faulty crank angle sensor, which can affect the engine timing and cause the fuel injection to be too rich or too lean. A rich fuel mixture is when there is too much fuel and not enough air in the cylinder, which can cause incomplete combustion and wasted fuel. A lean fuel mixture is when there is too little fuel and too much air in the cylinder, which can cause detonation and engine damage.
- Difficulty starting the engine: Difficulty starting the engine is the condition when the engine does not start easily or at all. Difficulty starting the engine can cause frustration and inconvenience. Difficulty starting the engine can be caused by a faulty crank angle sensor, which can prevent the ECU from receiving the crank angle signal and from controlling the engine timing and ignition. Without the crank angle signal, the ECU cannot tell when to fire the spark plugs and when to inject the fuel, which can prevent the engine from starting.
Conclusion
The crank angle sensor is a vital part of the engine that measures the crank angle and helps the ECU to control the engine timing and performance. The crank angle sensor is also useful for analyzing and diagnosing the engine problems. However, the crank angle sensor can also cause some problems if it is faulty or damaged, such as misfiring, poor fuel economy, and difficulty starting the engine. Therefore, it is important to maintain the crank angle sensor and to replace it when necessary.
Here are some tips for extending the life of the crank angle sensor:
- Check the crank angle sensor regularly and look for any signs of damage or wear, such as cracks, corrosion, dirt, or loose wires.
- Clean the crank angle sensor periodically and remove any dirt, dust, or debris that may interfere with the crank angle signal.
- Replace the crank angle sensor if it is faulty or damaged, or if it shows any symptoms of malfunction, such as a check engine light, an error code, or a poor engine performance.
- Use a quality crank angle sensor that is compatible with your vehicle and your engine type and design.
By following these tips, you can ensure the proper functioning of the crank angle sensor and the optimal performance of your engine.
Comments (0)
Please login to join the discussion
Be the first to comment on this article!
Share your thoughts and start the discussion